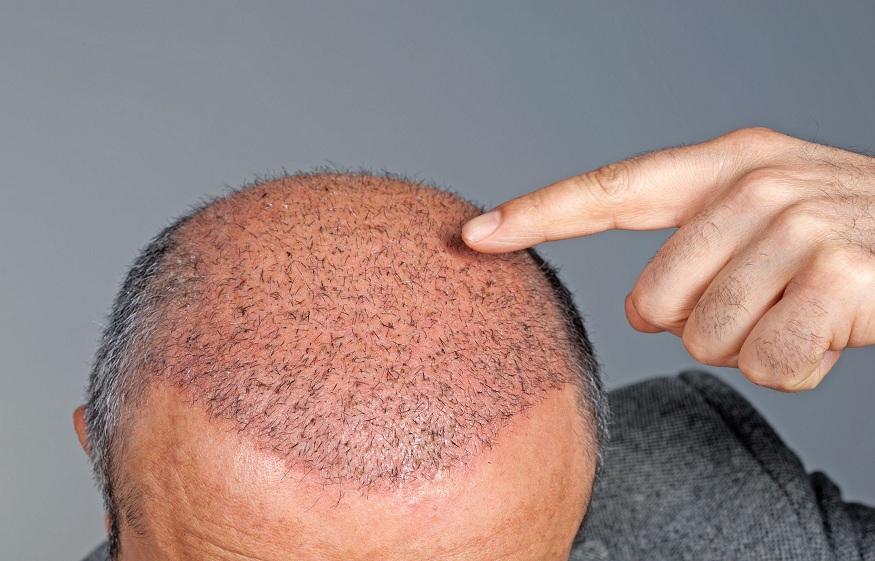
Overview
Hair transplant Islamabad procedures are done to add more hair to an area on your head where the hair might be thinning or balding. This procedure is done by extracting hair from the part of your scalp where hair growth is healthy, and implanting it to the area where hairs are thinning or having a bald area.
About 60 percent men and 50 percent experience hair loss problem worldwide. To overcome this problem, people often use different products such as topical treatments like minioxidil, some oral medications, gels and home remedies.
Hair transplant is one more restoration option available nowadays. The first transplant procedure was carried out in Japan in year 1939. In the following decades, physicians developed different techniques and over the time, surgeons started using mini- and micro-grafts to reduce the appearance of transplanted hair on the scalp.
Do hair transplants work?
Hair transplants are usually more successful than any other hair restoration methods. But there are some factors to look at:
- Around 10 to 80 percent of transplanted hair will regrow in three to four months approximately.
- Like regular hair, transplanted hair will get thinner with the passage of time or age.
- People with inactive hair follicles may have less effective transplants, but according to a recent study which suggests that plasma (PRP) therapy can be helpful to regrow the transplanted hairs completely.
- Hair transplants might not be practical for everyone. They are predominantly used to restore hair if you are losing or thinning naturally.
Most transplants are done by extracting your existing hair, so they might not be effective for treating people who are having:
- extensive thinning and baldness
- hair loss due to chemotherapy
- Hair loss due to medications
- Having thick scalp scars from wounds
How much do hair transplants cost?
Hair transplants cost depends on the following aspects:
- magnitude of the procedure
- availability of skilled surgeons in the area
- experience of the surgeon, and
- surgical technique
Post-operative care medications also add up to the final cost.
How does a hair transplant work?
In simple terms, a hair transplant takes hair you already have and transfers it to an area where you don’t have hair. It’s usually taken from the back of your head, but can also be taken from any other part of your body.
Your surgeon can choose any one of the transplant methods: FUT or FUE depending on the nature of the surgery.
Follicular unit transplantation (FUT)
FUT is also termed as Follicular Unit Strip Surgery (FUSS). In this procedure the surgeon removes healthy hair follicles in small strips from a donor area. The strips of follicles are then divided into hair grafts that will be implanted into the bald area. FUT requires a cut from where the hair strip is obtained at the donor area; this will result in minor scarring in the donor area. However, the strip is normally taken from back of the head where hair is thick, scarring won’t be easily visible.
The strip is then meticulously divided into tiny grafts individual follicular units comprised of one to four hairs by the help of an expert surgical team. These grafts are kept in ice-cold tissue storage solution until they are transplanted in the affected area.
The donor area is carefully stitched up after the surgery and it usually covered up by the surrounding hair. The stitches are removed after 10 to 14 days and the donor form a linear scar after healing completely.
Follicular unit extraction (FUE)
FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction) hair transplant is relatively advanced procedure in which follicular unit grafts, consisting of a small number of hair follicles, are individually removed from the naturally stronger areas of your scalp (the donor areas) and delicately placed to your affected areas (the recipient areas).
Firstly the surgeon will identify the recipient areas and devise a personalize plan to attain the most natural looking hairline.
Next, surgeon will trim the hair in the donor area to identify the healthy donor hairs. After the planning of donor area, the physician will remove individual follicular units from the scalp by making a tiny circular incision around them to isolate the graft.
Then he will extract the graft from the scalp using an instrument. Working with highly powered microscopes, trained technicians inspect the follicular grafts and arrange them for placement. Follicular units are arranged into groups and normally 1-4 hairs are commonly found within each follicle.
When the grafts are ready, the physician makes small incisions in the recipient area; the grafts are then delicately placed one by one, in order to achieve the most natural results according to the specific hair loss pattern.
Follicular Unit Excision (FUE) is comparatively more advanced technique, but both FUT and FUE methods provide excellent results.
Recovery
After the surgery you should follow the doctor’s instructions about caring for your scalp and any other self-care measures for speedy healing. You may have a large or small surgical dressing after the surgery that can be protected by a wearing a cap.
During the recovery period your scalp may be very tender. Your doctor may advise you to take pain medicines. Within 2 to 3 weeks after surgery, the transplanted hair will fall out, but they will regrow.
You may be prescribed to take the following:
- pain killers, such as ibuprofen
- antibiotics in order to avoid infections
- anti-inflammatories, such as an oral steroid, to get rid of swelling
- medications such as minioxidil to boost hair growth
Aftercare tips for hair transplant surgery:
- Only use mild shampoos.
- You should be able to return to your daily activities in about 3 days.
- Don’t press a brush or comb over the new grafts for almost 3 weeks.
- Don’t wear any hats until your doctor’s permission.
- Do not exercise for about a week.
- You do not need to worry if some hairs fall out as this is part of the process.
Hair transplant side effects
Potential side effects of Hair Transplants include:
- infections
- puss drainage around the surgical site
- scalp pain, itching, and swelling
- inflammation of hair follicles
- bleeding
- losing sensation around the surgical site
- irritated scalp
- dizziness
- chest pain
- headaches
- irregular heart rate
- hand, foot, or breast swelling